



Next: IETF Example Applications: NeTraMet,
Up: The IETF RTFM Working
Previous: The IETF RTFM Working
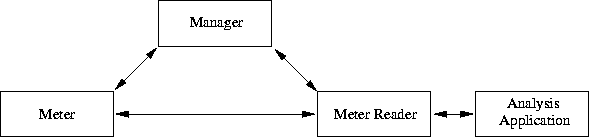
The architecture is based on an earlier model described in RFC1272
[8]. It distinguishes between a traffic
meter, a meter reader and a manager. Data is
analyzed by an analysis application which is not further
specified in the recommondations. Figure
3.2 gives an overview over the architecture.
Figure 3.2:
The RTFM Traffic Flow Measurement Architecture (RFC2063)
 |
The following terms are defined by the RFC and describe the basic structure
of the architecture:
- Manager
- A traffic measurement manager is an application which configures
``meter'' entities and controls ``meter reader'' entities. It uses the
data requirements of analysis applications to determine the
appropriate configurations for each meter and the proper operation of
each meter reader. It may well be convenient to combine the functions
of meter reader and manager within a single network entity.
- Meter
- The meter is the heart of a traffic flow measurement system. Meters are placed at measurement points determined by network operations personnel. Each meter selectively records network activity as directed by its configuration settings. It can also aggregate, transform and further process the recorded activity before the data is stored. The processed and stored results are called the ``usage data''.
- Meter Reader
- A meter reader reliably gets usage data from meters and makes it available to analysis applications.
- Analysis Application
- An analysis application processes the usage data
so as to provide information and reports which are useful for network
engineering and management purposes. Examples include:
- Traffic Flow Matrices, showing the total flow rates for many of the
possible paths within a network.
- Flow Rate Frequency Distributions, indicating how flow rates vary with time
- Usage Data showing the total traffic volumes sent and received by particular hosts.




Next: IETF Example Applications: NeTraMet,
Up: The IETF RTFM Working
Previous: The IETF RTFM Working
root
8/4/1997
